New Product Development is a comprehensive set of multi-disciplinary processes that turns an opportunity into a product to satisfy a customer.
What is New Product Development?
New Product Development (NPD) is a comprehensive multi-disciplinary process that transforms a market opportunity into a marketable new product to satisfy customer requirements.
According to Wheelwright and Clark (1992), NPD is defined as effective activity organisation and management to bring products to market with low development costs and short development times.
PDMA defines NPD as,
“A disciplined and defined set of tasks and steps that describe the normal means by which a company repetitively converts embryonic ideas into saleable products or services.”
PDMA handbook 2nd edition
It’s sometimes referred to as New Product Introduction (NPI) or new product planning and development, and it applies to tangible products such as phones, coffee makers, TV, etc. and intangible products like mobile phone apps, software programs, etc.
Why is New Product Development necessary?
NPD is the driving force of companies and vital for their organic growth. Insatiable consumer appetite, strong worldwide competition, and changing consumer behaviour and technology force companies to invest in new products to succeed or for their survival.
The importance of introducing new products can be summarised in these “Seven reasons why new product development is necessary.”
- Changing consumer
- Increasing competition
- Technological advancement
- New opportunities (growth and development)
- Risk diversification
- To increase company & brand reputation
- To utilise excess capacity
Importance of New Product Development strategy
Why do you need a thorough NPD strategy? Consider these 4 statistical facts about how products fair according to data from Mckinsey global institute.
- Only 4 in 7 product ideas enter the product development stage
- Only 3 products get launched from 14 product ideas
- Only 1 in 7 product ideas will yield a successful product
- Launched products have a failure rate of 25% to 45%
Research shows that some NPD failures can be attributed to the lack of a structured NPD process. According to Wheelwright and Clark (1992), companies who approach NPD in a structured manner have more success than those with an ad-hoc approach.
By following a well-planned set of procedures & milestones, companies can avoid some of the common pitfalls that lead to the failure of NPD, such as;
- Overestimate market size
- Customer requirement misinterpretation
- Launched at the wrong time
- Poor product design
- Target customer’s requirement mismatch
- Price too high
- Poor advertising and marketing
- High product development cost due to overrun & resource overuse
- Competition risks and threats
New Product Development models
A well-tailored NPD strategy will enable companies to organise their product planning, understand their customers, accurately plan and efficiently use its resource for NPD. An NPD strategy will also help to avoid the above-mentioned pitfalls and increase the chance of product success.
| Models | Phases |
| Roozenburg & Eekels, 1995 | Analysis – Concept – Materialisation |
| IEC60300-1 | Concept and definition – Design and development – Manufacturing and installation |
| Fox, 1993 | Pre-concept – Concept – Design – Demonstration – Production |
| Pahl & Beitz, 1996 | Clarification of task – Conceptual design – Embodiment design – Detail design |
| Cooper, 2005 | Scoping – Build business case – Development – Testing and validation – Launch |
| Blanchard, 2004 | Conceptual design – Preliminary system design – Detailed design and development – Construction – Production |
| Pugh, 1990 | Market – Specification – Concept design – Detail design -Manufacture |
| Andreasen & Hein, 1987 | Recognition of need – Investigation of need – Product principle – Product design – Product preparation – Execution |
There are various models proposed by authors before, but all start with an idea to build a product that meets the customer’s technical specifications and ends with a product launch or introduction to the market. The number of stages, phases and their description varies from model to model depending on the following.
- Product type (tangible/intangible)
- The degree of innovation (redesign vs routine design).
- Product Complexity
- Production & manufacturing process – manual or automated
- Supply chain
- Technology involved.
- Resource availability (manpower) Labour availability?
- Time and budget
As the table above shows, the product development stages can vary but they often can be grouped into these 5 key phases which include 8 important activities;
- Fuzzy front end
- Opportunity identification & analysis
- Idea generation & screening
- Concept & technology development
- Business case building
- Marketing strategy development & Marketing mix
- Business analysis
- Product design
- Product design
- Product Implementation
- Test marketing
- Commercialisation/Fuzzy back end
- Product launch
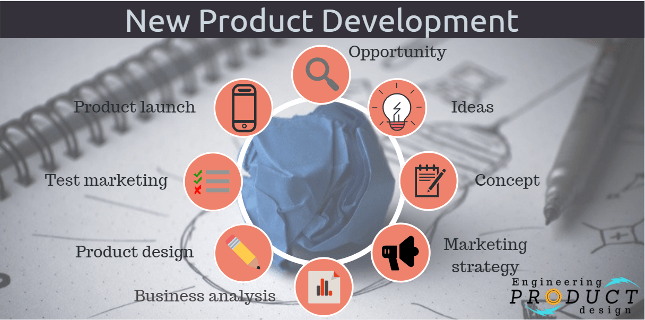
Five key New product development stages
Fuzzy Front end
As the name suggests, the fuzzy front end is the messy stage of the new product development where opportunities are identified & analysed, and ideas are generated & screened before a viable concept is developed. This set of activities paves the way for a formal technical specification of the final product.
Business case building
Before the product design and development begins, this stage analyses the market. Marketing strategy development defines the target market, sales & market share. At this stage, the company must also determine the best market mix ( 4Ps – Product, place, price & Promotion). Finally, the company evaluates the attractiveness of the proposed product against the company’s long-term objectives.
Product design
The product design stage is the detailed phase where the technical requirements are turned into an engineering product design. In engineering, prototyping and product design are at the heart of any product development and generally follow the following four phases.
Product Implementation
Market testing – Stage at which the product is introduced using the proposed marketing program. It lets the company test the product and its marketing program—targeting and positioning strategy, advertising, distribution, pricing, branding and packaging, and budget levels.
Commercialisation
After the product implementation phases, management will have gathered all the relevant information to make the final decision about going commercialisation. At this stage, companies use the knowledge gained from the product implementation stage and their marketing mix to launch the product, where product life cycle management starts.