Design for Manufacture & Assembly (DfMA) is an engineering design methodology designers and manufacturers should use to minimise cost and increase the quality of product designs.
Contents covered in this article
What is Design for Manufacture and Assembly?
DfMA is a design methodology that emphasises manufacturing simplicity and assembly efficiency. As a result, a product’s design can be improved to enable faster, safer, more cost-effective, and more efficient manufacturing and assembly.

Design for Manufacture and Assembly consists of two primary methodologies. One for manufacturing and another for assembly. They are Design for Manufacture (DFM) and Design for Assembly (DFA). DFM and DFA aim to optimise design while lowering labour, materials, and overhead costs.
What is Design for Manufacture?
DFM entails designing a product’s parts to be as simple to manufacture as possible. Therefore, choosing the most economical materials and production methods is essential, reducing the manufacturing process’s complexity.
Principles of DfM
- The parts should be made to fit within the tolerance limits of the manufacturing process.
- The part should be defined as a manufacturing process at an early stage
- Part features should be within the capabilities of the chosen manufacturing process
- A designer should explore and improve all manufacturing functions, including fabrication, assembly, testing, procurement, shipping, service, and repair of parts and assembly
What is Design for Assembly?
Dfa entails designing a product to be simple to assemble. It focuses on minimising the number of assembly operations and lowering the cost of product assembly.
Typical products go through the following stages and checks.
- Designed
- Prototypes
- Tested
- Manufactured or procured
- Inspected
- Controlled
- Documented
- Life cycle managed
Since each part you design and introduce has to go through the above stages, the cost of managing a single component adds up; hence reducing the part is the most significant function of the DFA.
Principles of Design for Assembly
Recommendation by Ulrich & Eppinger (1995)
- Reduce part count and part types
- Strive to eliminate adjustments
- Design parts to be self-aligning and self-locating
- Ensure adequate access and unrestricted vision
- Ensure the ease of handling of parts from bulk
- Minimise the need for reorientations during assembly
- Design parts that cannot be installed incorrectly
- Maximise part symmetry if possible or make parts asymmetric
- Eliminate processing steps
- Choose the appropriate economic scale for the process
- Standardise components and processes
- Adhere to “Black Box” component procurement (describe what the component has to do, not how to achieve it)
- Minimise system complexity
Advantages and Disadvantages of Design for Manufacture and Assembly
Advantages of DfMA
- Reduced waste
- Lower manufacturing
- Fewer design changes during the later stages of the design process
- DfMA significantly reduced the assembly cost by using fewer parts, requiring less labour, and using fewer unique parts.
Disadvantages of DfMA
- Prices rise due to high startup costs for factories and a lack of demand for mass-produced goods.
- Design for manufacture and assembly methodology is not always the cheapest option as it depends on quantity.
Design for Assembly classification system
Design for Assembly (DFA) manual handling classification systematically quantifies how features affect the manual handling of parts during assembly.
What is the Design for assembly classification?
So what is Design for Assembly? It can be defined as a method of designing items with the simplicity of assembly in mind.
Design for assembly should be considered at all 4 stages of the product design process, especially during the embodiment stage of the design.
It’s difficult to analyze and compare design solutions systematically without a methodology to quantify an engineering product design. To overcome this issue Boothroyd and Dewhurst came up with a system to quantify a design using simple manual assembly techniques.
Boothroyd and Dewhurst’s classification system, systematically quantify how features affect the manual handling of the part during the assembly. They divided the classification and assembly method into two main categories. Manual handling and manual insertion and graded them according to how difficult it is to handle and insert by allocating time for each activity.
Full classification and definition can be found in their book (“Product design for manufacture and assembly” (Boothroyd Dewhurst Inc 1999)
Benefits of a DFA classification system
- It quantifies the process
- Quick results
- Simple and easy to use
- It eliminates subjective judgment during the design review
- Ideas, reasoning, and decision during this review can be documented
DFA Manual handling times
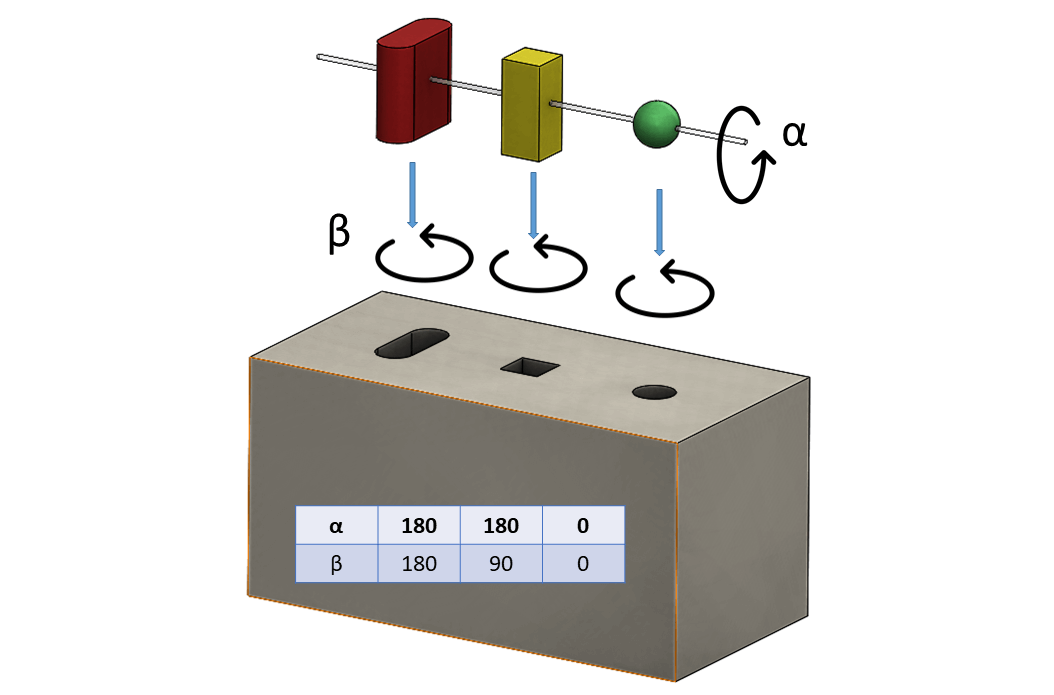
One hand without tools
| One hand | Parts are easy to grasp & manipulate | Parts present handling difficulties | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parts can be grasped and manipulated by one hand without the aid of grasping tools | Thickness > 2 mm | Thickness ≤ 2 mm | Thickness > 2 mm | Thickness ≤ 2 mm | |||||||
| Size > 15 mm | 6 mm ≤ Size > 15 mm | Size < 6 mm | Size > 6 mm | Size ≤ 6 mm | Size > 15 mm | 6 mm ≤ Size > 15 mm | Size < 6 mm | Size > 6 mm | Size ≤ 6 mm | ||
| 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | ||
| (α + β) < 360 ° | 0 | 1.13 | 1.43 | 1.88 | 1.69 | 2.18 | 1.84 | 2.17 | 2.65 | 2.45 | 2.98 |
| 360° ≤ (α + β) < 540 ° | 1 | 1.5 | 1.8 | 2.25 | 2.06 | 2.55 | 2.25 | 2.57 | 3.06 | 3 | 3.38 |
| 540° ≤ (α + β) < 720 ° | 2 | 1.8 | 2.1 | 2.55 | 2.36 | 2.85 | 2.57 | 2.9 | 3.38 | 3.18 | 3.7 |
| (α + β) = 720 ° | 3 | 1.95 | 2.25 | 2.7 | 2.51 | 3 | 2.73 | 3.06 | 3.55 | 3.34 | 4 |
Table 1. DFA Manual handling times – one hand without tools (Boothroyd, Dewhurst, & Knight, 2011)
One hand with tools
| One hand with grasping aids | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parts can be grasped and manipulated by one handle but only with the use of grasping tools | Parts need tweezers for grasping and manipulation | Parts need standard tools other than tweezers | Parts need special tools for grasping and manipulation | |||||||||
| Parts can be manipulated without optical magnification | Parts require optical magnification for manipulation | |||||||||||
| Parts are easy to grasp and manipulate | Parts present handling difficulties (a) | Parts are easy to grasp and manipulate | Parts present handling difficulties (a) | |||||||||
| Thickness > 0.25 mm | Thickness ≤ 0.25 mm | Thickness > 0.25 mm | Thickness ≤ 0.25 mm | Thickness > 0.25 mm | Thickness ≤ 0.25 mm | Thickness > 0.25 mm | Thickness ≤ 0.25 mm | |||||
| 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | |||
| α≤180° | 0≤β≤180° | 4 | 3.6 | 6.85 | 4.35 | 7.6 | 5.6 | 8.35 | 6.35 | 8.6 | 7 | 7 |
| β=360° | 5 | 4 | 7.25 | 4.75 | 8 | 6 | 8.75 | 6.75 | 9 | 8 | 8 | |
| α=360° | α≤β≤80° | 6 | 4.8 | 8.05 | 5.55 | 8.8 | 6.8 | 9.55 | 7.55 | 9.8 | 8 | 9 |
| β=360° | 7 | 5.1 | 8.35 | 5.85 | 9.1 | 7.1 | 9.55 | 7.85 | 10.1 | 9 | 10 | |
Table 2. DFA Manual handling times – one hand with tools (Boothroyd, Dewhurst, & Knight, 2011)
With both hands
| Two hands for manipulation | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parts severely nest or tangle or are flexible but can be grasped and lifted by one hand ( with the use of grasping tools if necessary)(b) | Parts present no additional handling difficulties | Parts present additional handling difficulties (Sticky, delicate, slippery etc) (a) | ||||||||
| α ≤ 180° | α = 360° | α ≤ 180° | α = 360° | |||||||
| Size > 15 mm | 6 mm ≤ Size > 15 mm | Size < 6 mm | Size > 6 mm | Size ≤ 6 mm | Size > 15 mm | 6 mm ≤ Size > 15 mm | Size < 6 mm | Size > 6 mm | Size ≤ 6 mm | |
| 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | |
| 8 | 4.1 | 4.5 | 5.1 | 5.6 | 6.75 | 5 | 5.25 | 5.85 | 6.35 | 7 |
Table 3. DFA Manual handling times – one hand with tools (Boothroyd, Dewhurst, & Knight, 2011)
Both hands and assistance for large parts
| Two hands or assistance required for large size | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Two hands or persons or mechanical assistance required for grasping and transporting parts | Parts can be handled by one person without mechanical assistance | Parts severely nest or tangle or are flexible (b) | Two persons or mechanical assistance required for parts manipulation | ||||||||
| Parts do not severely nest or tangle and are not flexible | |||||||||||
| Part weight < 10 lb ( ≈ 4.5 kg) | Parts are heavy ( > 10lb (≈ 4.5 kg)) | ||||||||||
| Parts are easy to grasp and manipulate | Parts present handling difficulties (a) | Parts are easy to grasp and manipulate | Parts present handling difficulties (a) | ||||||||
| α ≤ 180° | α = 360° | α ≤ 180° | α = 360° | α ≤ 180° | α = 360° | α ≤ 180° | α = 360° | ||||
| 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | ||
| 9 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 5 | 7 | 9 | |
Table 4. DFA Manual handling times – one hand with tools (Boothroyd, Dewhurst, & Knight, 2011)
References
Boothroyd, G., Dewhurst, P., & Knight, W. A. (2011). Product design for Manufacture and Assembly. London: CRC Press.