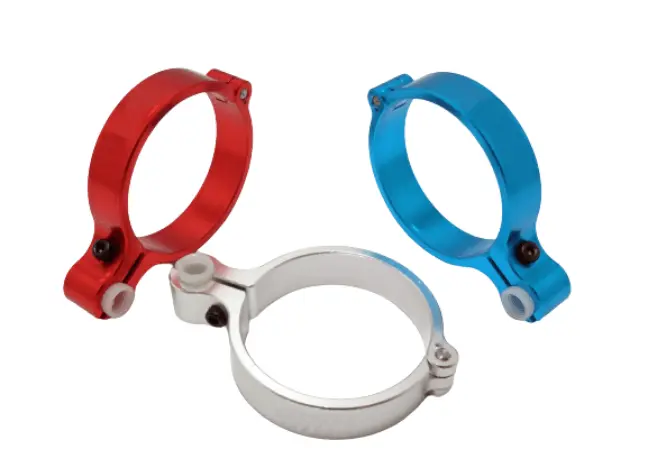
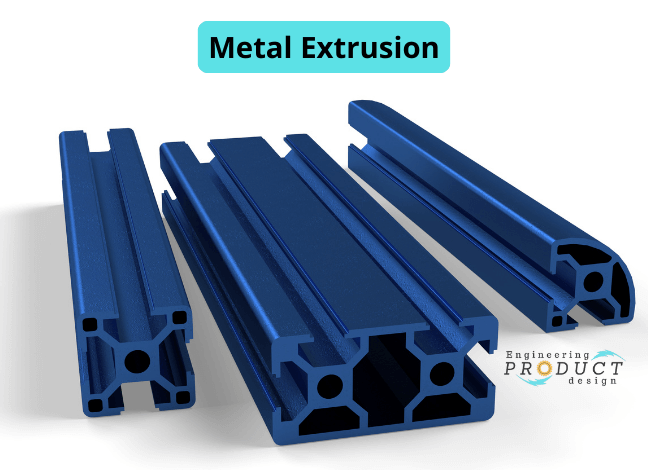
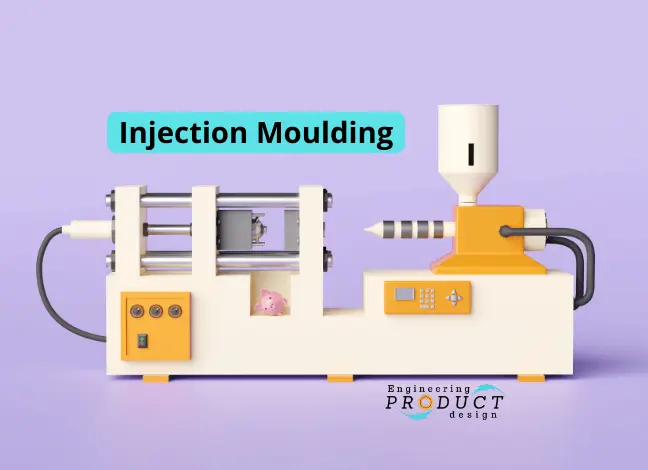
Designing for CNC machining: Material Selection and Geometric Constraints
Achieving CNC precision requires careful material selection and attention to geometric constraints. This guide explores how these factors impact machining accuracy, cost, and performance, offering practical tips for designing high-quality components.
Designing for CNC machining: Material Selection and Geometric Constraints Read More »