Liquid Silicone Rubber moulding is suitable for manufacturing complicated geometries and can combine multiple functional elements into a part.
What is Liquid silicone rubber moulding?
Liquid Silicone Rubber (LSR) moulding, sometimes known as Liquid Injection Moulding (LIM), is a thermoset process of two compounds mixed and then heat-cured inside the mould using a platinum catalyst to create flexible silicone parts. A low compression set and the ability to resist extreme temperatures make LSR mouldings durable and ideal for challenging applications. LSR elastomer offers exceptional optical clarity, durability, and design flexibility while maintaining excellent mechanical properties across a wide range of temperatures (-50oC to 250oC).

LSR injection moulding is suitable for manufacturing complicated geometries and can combine multiple functional elements into a single part due to its design and tooling flexibility. LIM provides considerable advantages in terms of product dependability and the total cost of tooling.
How does LSR different from Injection moulding
LSR moulding is very similar to conventional injection moulding in how the part is formed inside a mould but varies in how it cures the part.
In injection moulding, Thermoplastic resin is melted before injection and cured using pressure. LSR is a two-part thermoset compound that is cooled before being injected into a heated mould and ultimately cured into a final part. Moulded state of thermoset LSR is permanent and cannot be remelted and used again like a thermoplastic. The components A and B are combined in a 1:1 ratio to generate the heat-accelerated reaction that converts liquid to solid rubber.
How does the LSR moulding process work?
As shown in the image below, a liquid injection moulding machine consists of pair of supply drums or plungers, an injector, a metering pump, a static cold mixer, a nozzle, and the heated mould.
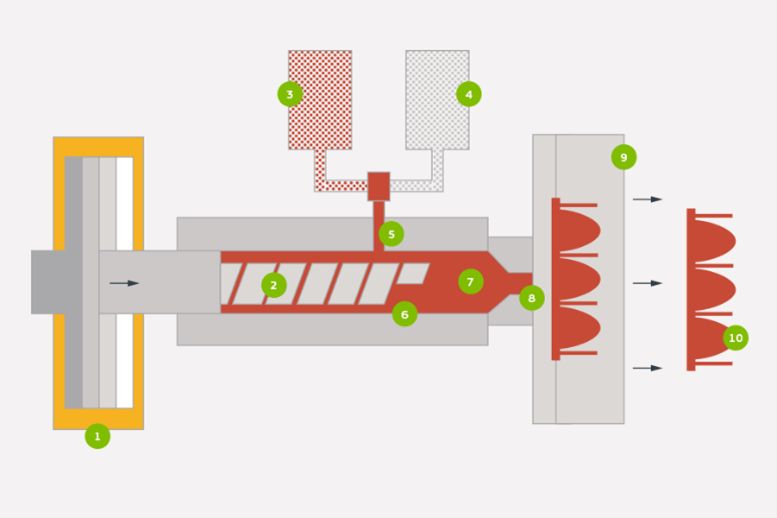
- First, the base-forming silicone and the platinum catalyst parts of the liquid silicone rubber compounds (A & B) are added to the pumping system using the supply drums. These are also called Plungers and serve as primary containers for both compounds. A separate container holds the additives and colour pigments.

- The injectors then pressurize the liquid silicone to help inject material into the machine’s metering pumps. Then, pressure and injection rates are manipulated to increase process repeatability and accuracy.
- The metering pump or unit will then mix the two liquid components, the catalyst, and the base-forming silicone, ensuring that the two materials retain a consistent ratio (1:1) while being delivered simultaneously.
- Then, base-forming silicone, catalyst, additives and pigments are pumped into the nozzle via the cold runner static mixer.
- From the metering section and mixer, the mixed compound is pushed through the cooled runner systems via the nozzle into the heated mould cavity, where the vulcanization takes place to create the pars. A nozzle aids the deposition of the mixture into the mould. The nozzle frequently has an automated shut-off valve to avoid leakage and mould overfilling.
- A mould clamp secures the mould throughout the injection moulding process and opens the mould once the procedure is finished.
Liquid silicone rubber applications
Liquid silicone rubber is versatile and used in a wide range of applications, from consumer electronics to extreme industrial applications.

- Optics – Outdoor, automotive, and professional lighting
- Automotive – Lenses LED lighting, Light guides, Optical coupling, O-rings, buttons, components, gaskets, and wire harness components
- Electronics – LED lenses, Light guides, Protective sleeves
- Consumer goods – Nose pads, Ear bugs, Google, Headsets
- Healthcare and Medical – Medical tubing, Endoscopy components, Catheters, Lenses, UV LED lighting, flow control valves, syringe stoppers, and other components
Advantages and disadvantages of LSR and LIM
The following advantages and disadvantages are for LSR mouldings and the LIM process.
Advantages of Liquid silicone rubber
- Its low viscosity will allow the material to flow easily into thin and complex areas of the mould.
- Superior compatibility with human tissue and body fluids
- Excellent chemical resistance
- Suitable for high-volume production
- Excellent mechanical characteristics, including good elongation, excellent tear strength, high tensile strength, and a wide hardness range (5-80 Shore A).
- Process repeatability
- Short cycle time compared to compression moulding
- resistance to bacteria growth
- Process easily automated
- The ability to sterilize makes LSR suitable for medical and healthcare products.
- Adheres to rigorous FDA guidelines
- Great resistance and stability in the most consumer environment
- Excellent resistance to high temperatures than thermoplastics
- Suitable for complex and high-precision parts
- High tear and tensile strength
Disadvantages of Liquid silicone rubber
- Once LSR cures, it cannot be moulded again, hence can’t recycle LSR
- High production time and cost
- Sticky feel if untreated making them attract dust and other particles
- They are not suitable for submerged applications in alcohol or gasoline
- when exposed to some materials, such as sulfur and latex, LSR will inhibit its curing
- Limited choice of material for LIM process
- Silicone has limited grades to choose