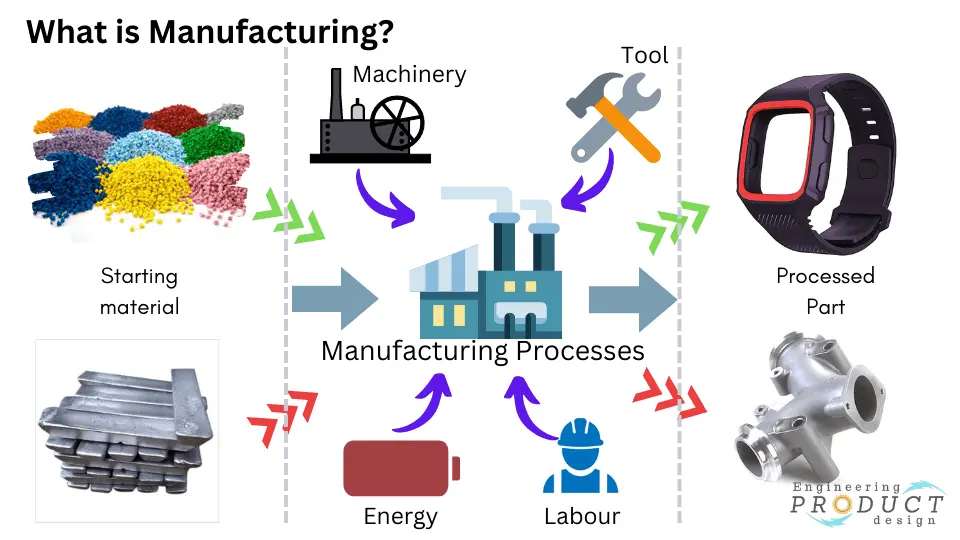
Manufacturing is the production of goods from raw materials using energy, labour, machinery, tools, and manufacturing processes.
What is Manufacturing?
Manufacturing is a large-scale production of goods using energy, manual labour, machinery, tools, and manufacturing processes to convert raw materials, parts, and components into finished items by changing geometry, properties, and appearance.
Modern-day engineering products are complex and comprise various material combinations, electronics control boards, wires, batteries and charging ports. Hence, modern-day manufacturing also includes assembling these elements to create the finished product.
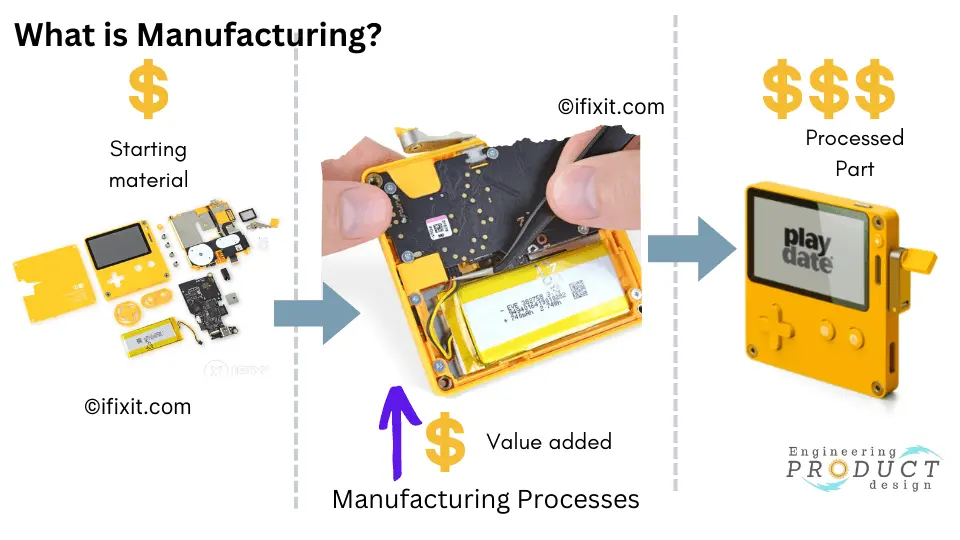
Economically, manufacturing can be defined as the economic transformation of materials into items of better value through one or more processing and assembly operations. The critical point is that production adds value to a starting material or element by changing its form, fit and function to satisfy end users’ requirements.
Manufacturing types
There are three main manufacturing types in how businesses produce products. They are Make-to-Stock (MTS), Make-to-Order (MTO), and Make-to-Assemble (MTA).
Make-To-Stock (MTS)
Make-to-stock is a traditional strategy that businesses use to match inventory to expected consumer demand. For example, a company would estimate consumer demand for the product and produce to stock them to meet the estimated demand.
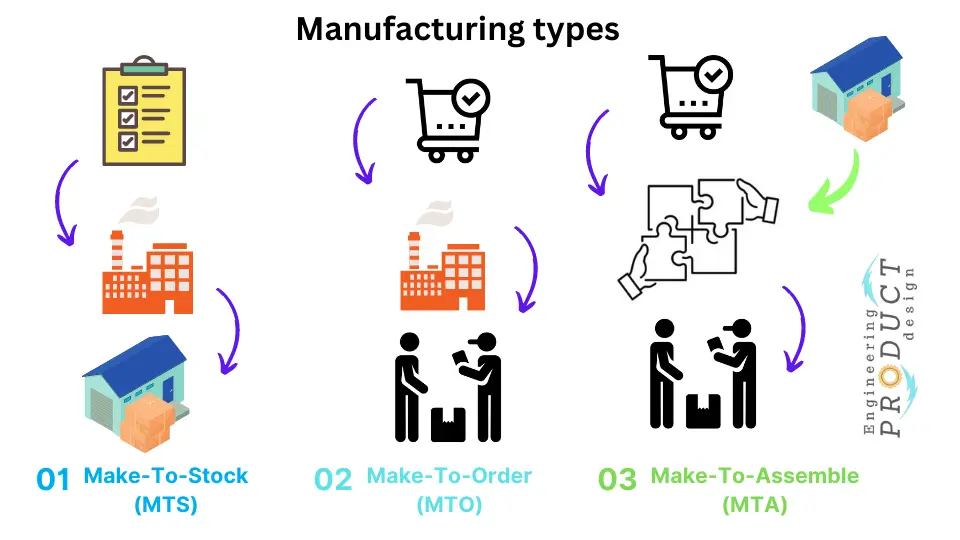
Make-To-Order (MTO)
Make-to-order, sometimes called made-to-order, is a manufacturing strategy that generally begins only after the consumer purchases the product. MTO benefits include customer customisation, reduced stock obsolescence, reduced finished goods inventory, and reduced overall waste.
Make-To-Assemble (MTA)
Make-to-assemble, also called assemble-to-order, is a business strategy in which products are quickly produced from stocked parts only when an order is confirmed. MTA is a hybrid of make-to-order and make-to-stock methods.
Manufactured product types
Products fall into Consumer and Capital goods. As the name suggests, consumer goods are products manufactured to sell directly to the customer, such as Smartphones, TVs, Drones and Laptops.
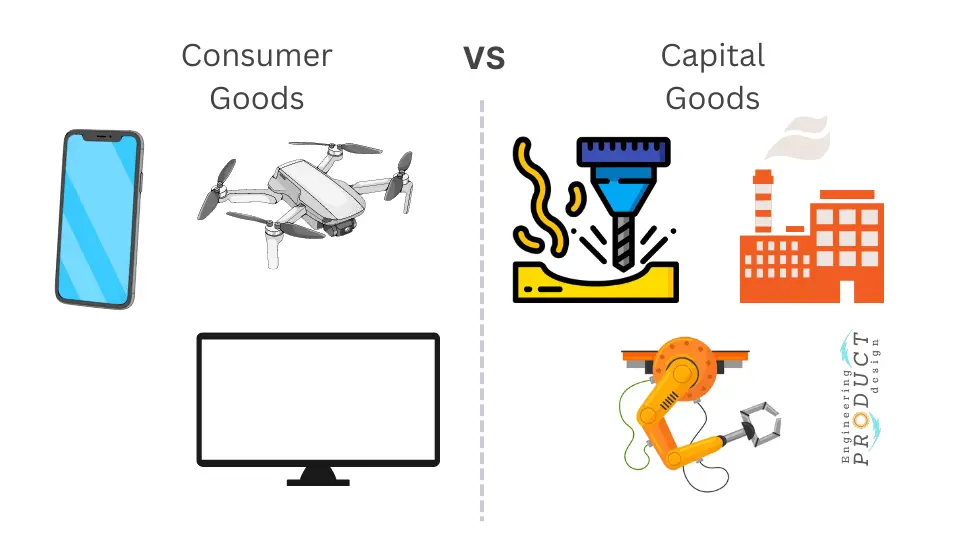
Capital goods are items companies and businesses purchase to make products for consumers or other capital goods such as CNC machines, Injection moulding machines, and Factory equipment.
This article details Capital goods in more in-depth.
Production vs Manufacturing
The words manufacturing and production are often used interchangeably in the industry. Manufacturing converts raw materials into finished goods using machinery, tools and human resources. On the other hand, production refers to the processes or methods that convert inputs, such as raw materials and semi-finished components, into products and services, which may or may not involve using tools, machinery and human resources.
Net-shape and Near-net-shape
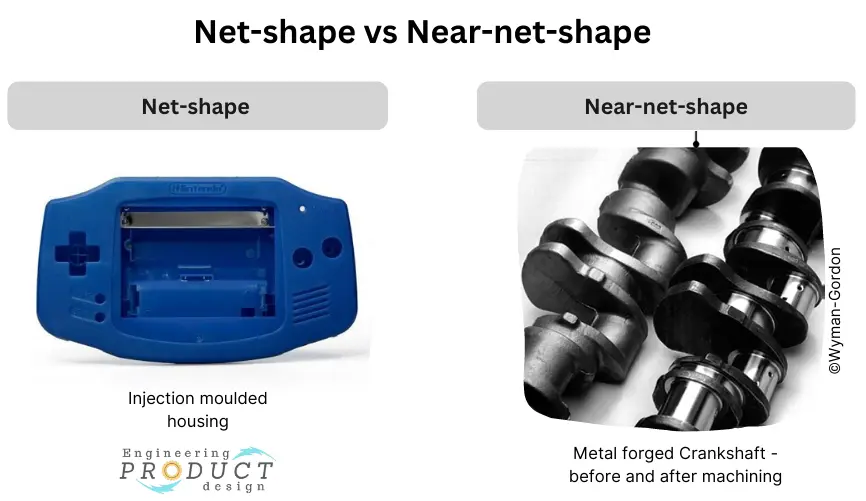
Net-shape and near-net-shape manufacturing are methods for producing a part in a single operation with the final specified dimensions, tolerances, and surface finish. For example, a cast, forged gear, or crankshaft typically lacks the required dimensional properties, necessitating extra processing such as machining or grinding. These additional activities can dramatically increase the cost of a product.
What is Near-net-shape manufacturing?
Near net shape (NNS) refers to manufacturing processes that convert raw material into a component that is as close to the finished product as possible in size and shape. Depending on the part design and features, processes like Sand casting, die casting, and investment casting can be examples of Near net shape as they might need features like threads and bearing surfaces machined after the initial process.

What is Net-shape manufacturing?
Net shape processes are primary processes that convert raw material into parts with no subsequent machining or different techniques required to achieve the final shape and size. An Injection moulding part is an example of a Net-shape manufactured part.

Precision casting, forging, shaping sheet metal, vacuum casting, powder metallurgy, additive manufacturing and injection moulding of metal powders, and injection moulding of polymers are typical instances of net-shape production.
What are Manufacturing Processes?
Manufacturing processes create value-added engineering products and components using physical and chemical processes to change a starting material’s geometry, characteristics, and appearance.
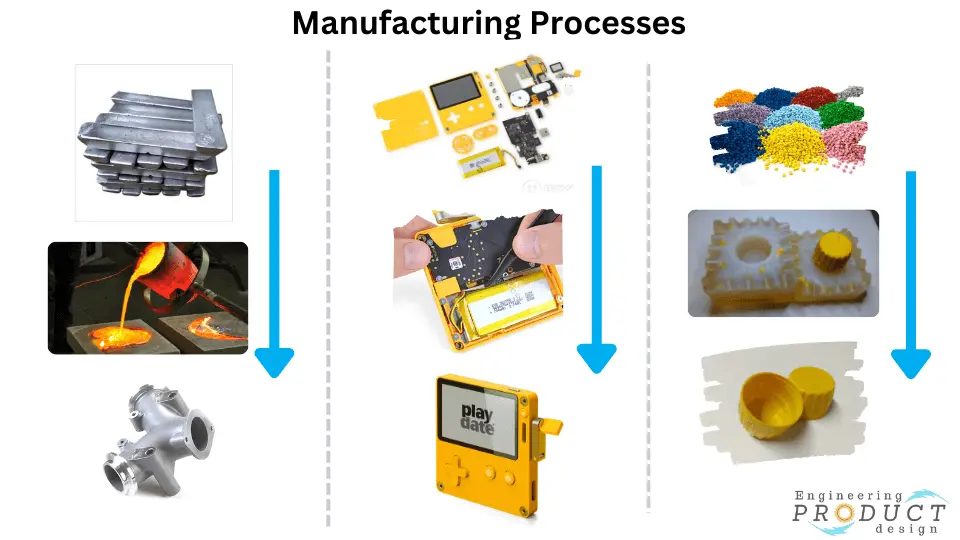
Manufacturers typically carry out the processes as a unit operation, which means it is a single step in a series of steps required to transform a starting material into a finished product. Processing operations and assembly operations are the two basic types of manufacturing operations.
Solidification processes, Metal forming, machining, Particulate processing, Heat treatments, Welding, Laser marking, Adhesive bonding and mechanical fastening are some of the widely used Manufacturing processes in the industry.