Pillow block bearing units are housed bearings with a machined mounting surface. They support shafts in mechanical transmission.
Contents covered in this article
What is a Pillow Block Bearing?
Pillow block bearing units are usually housed bearings with a machined mounting surface and are used in mechanical power transmission systems to support shafts and couplings. The shaft is parallel to the mounting surface and generally perpendicular to the mounting screws. They are a type of housed-bearing unit. These could have different bearings, such as ball bearing, cylindrical bearings, tapered rollers or synthetic bushings. They are crucial components in various machinery, ensuring shafts remain in position and operate smoothly.
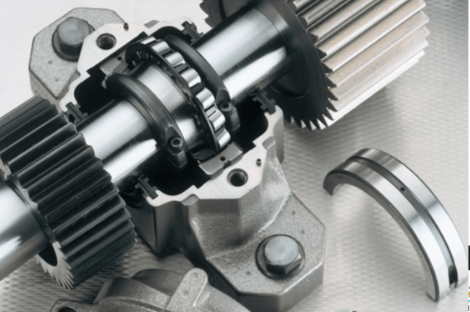
Design and Functionality
These units typically consist of a bearing mounted in a housing that provides a stable platform for the shaft. Depending on the application’s requirements, the bearings inside can be ball bearings, cylindrical bearings, tapered rollers, or synthetic bushings. The housing can be solid or split, allowing for easier installation and maintenance.
Pillow Block vs. Plummer Block
They are sometimes identified as “Pummel blocks”, although their construction is marginally different. It is essential to differentiate between pillow block and plummer block bearing units. While both serve similar purposes, pillow blocks are designed for light to medium load applications, whereas plummer blocks are suited for higher loads and industrial use. The construction materials and bearing types may vary based on their intended application.
Types of Pillow Block Bearings
Pillow block bearings can be classified based on housing construction and the type of bearing used.
Housing Construction
- Solid Housed Bearings: These are single-piece housings that provide greater rigidity and are often used in applications where bearing replacement is infrequent.
- Split-Housed Bearings: These two-piece housings allow for easier bearing replacement and are beneficial in applications where maintenance access is critical.


Types of Bearings
- Plain Bearings: These plain bearing versions suit applications with lower speeds and loads.
- Ball Bearings: These are commonly used due to their versatility and ability to handle radial and axial loads.
- Roller Bearings:
- Tapered Roller Bearings: Ideal for applications with high radial and axial loads.
- Spherical Roller Bearings: These can accommodate misalignment and are used in heavy-duty applications.
- Cylindrical Roller Bearings: Provide high radial load capacity and are used in high-speed applications.
Housing Materials for Pillow Block Bearings
The housing material for pillow block bearings is critical for ensuring durability and performance in various environments.
- Cast Iron: Widely used due to its strength and cost-effectiveness. Suitable for general applications.
- Stainless Steel: Offers excellent corrosion resistance and is ideal for applications in food processing or environments exposed to moisture.
- Thermoplastic: Provides good chemical resistance and is used in applications requiring lightweight and non-corrosive materials.
How to Select Pillow Block Bearings
Selecting the appropriate pillow block bearing involves several factors:
- Load Type – Determine the radial and axial loads the bearing will support.
- Bearing Type – Plain bearing, Ball-bearing, Roller bearings – Tapered roller bearing, Spherical- roller bearings, Cylindrical roller bearings
- Shaft attachment – Units can have a set screw, eccentric lock, single or double set collar, concentric lock or tapered adapter
- Seals – Seals vary as well, including clearance seals, light contact, heavy contact and auxiliary-type seals
- Shaft Size – Ensure the bearing matches the shaft diameter.
- Running Speed – Higher speeds may require specific bearing types.
- Misalignment – Choose bearings that can accommodate shaft misalignment if present. Consider both Static and dynamic misalignment.
- Environment – Consider factors like temperature, moisture, and exposure to chemicals.
- Mounting Style – Decide between solid or split housings based on ease of installation and maintenance.
Key Factors in Sizing Pillow Block Bearings
Accurate sizing of pillow block bearings involves considering several factors:
Load Type and Capacity
- Radial Load: The load perpendicular to the shaft. Common in applications like conveyor belts.
- Axial Load: The load parallel to the shaft. It is found in applications with a push or pull along the shaft’s length.
- Combined Load: A combination of radial and axial loads. Most common in real-world applications.
Note: Exceeding the bearing’s rated load capacity can lead to premature failure.
Shaft Diameter
The shaft diameter must fit the bearing bore precisely. Standard shaft sizes are available, but custom sizes can be specified. The fit between the shaft and the bearing is crucial for preventing slippage and ensuring smooth operation.
Speed Rating
The bearing’s operational speed should be within its specified speed rating. High-speed applications may require specific bearing types to handle greater rotational speeds without overheating or excessive wear.
Misalignment Tolerance
Consider how much misalignment the bearing can tolerate without affecting performance. Misalignment can cause increased friction and wear, leading to bearing failure. Pillow block bearings with spherical bearings can accommodate some misalignment.
Environmental Conditions
- Temperature: Ensure the bearing can operate within the temperature range of your application.
- Contamination: Bearings used in dirty or corrosive environments may require special sealing and materials.
- Humidity: Stainless steel or other corrosion-resistant materials may be necessary in humid environments.
Detailed Sizing Process
Step 1: Identify Application Requirements
Start by understanding the specific requirements of your application, including:
- Load type (radial, axial, or combined)
- Operating speed
- Environmental conditions (temperature, contamination, etc.)
- Shaft diameter
Step 2: Calculate Load
Determine the actual load the bearing will need to support. This includes:
- Static Load: The load when the bearing is stationary.
- Dynamic Load: The load when the bearing is in motion.
Use the following formulas to estimate the dynamic equivalent load (P):
\[ P = X \cdot F_r + Y \cdot F_a \]Where:
– \( F_r \) = Radial load– \( F_a \) = Axial load– \( X \) and \( Y \) are factors dependent on the bearing type and load conditions (typically provided by the manufacturer).Step 3: Determine Shaft Size
Measure or specify the shaft diameter that the bearing will support. Ensure the shaft fits the bearing bore snugly, and consider using an interference or clearance fit based on the application.
Step 4: Select Bearing Type
Choose the appropriate bearing type based on:
- Load capacity (radial and axial)
- Speed rating
- Misalignment tolerance
- Environmental factors
Common bearing types include plain, ball, and roller bearings.
Step 5: Verify Housing and Mounting Requirements
Ensure that the housing and mounting configuration matches your application. Consider factors such as:
- Housing Material: Based on the environment (e.g., cast iron, stainless steel).
- Mounting Style: Solid or split housings.
- Attachment Methods: Set screws, eccentric locks, tapered adapters, etc.
Step 6: Evaluate Sealing and Lubrication Needs
Proper sealing and lubrication are critical for bearing performance. Choose seals based on environmental exposure:
- Clearance Seals: Minimal contact, suitable for low-contamination environments.
- Light Contact Seals: Balance between protection and friction.
- Heavy Contact Seals: Maximum protection for high-contamination environments.
Determine the lubrication method (grease or oil) and maintenance intervals.
Applications of Pillow Block Bearings
Pillow block bearings are versatile components used in various industries and applications, such as paper machines, ventilation systems, rolling mills, conveyor belt rollers, and belt drives connecting motors and pumps.
- Manufacturing: Used in conveyor systems, machinery, and assembly lines to support rotating shafts.
- Agriculture: Found in equipment such as tractors, harvesters, and balers.
- Automotive: Utilized in vehicles for supporting shafts in engines and transmissions.
- Food Processing: Essential in food production lines where hygiene and corrosion resistance are crucial.
- Mining: Used in heavy machinery for ore processing and transport.
Installation Guide for Pillow Block Bearings
Proper installation is vital for the longevity and performance of pillow block bearings. Follow these steps for effective installation:
- Preparation: Ensure the mounting surface is clean and free from debris. Verify shaft dimensions and alignment.
- Mounting: Position the bearing on the shaft and align it with the mounting holes. Secure the bearing using the appropriate bolts or screws.
- Lubrication: Apply the recommended lubricant to reduce friction and wear.
- Testing: After installation, rotate the shaft to ensure smooth operation and check for unusual noises or vibrations.
Watch the Rexnord How to Install a Pillow Block Bearing video for a detailed visual guide.
Advantages and Limitations

Advantages of Pillow block bearings
- Ease of Installation: Pillow block bearings are designed for straightforward installation, reducing downtime.
- Versatility: Suitable for various applications due to the variety of available bearing types and housings.
- Maintenance: Split housings allow for easy maintenance and replacement of bearings.
Limitations of Pillow block bearings
- Load Capacity: Pillow block bearings may not be suitable for extremely high-load applications compared to Plummer blocks.
- Environmental Limitations: Standard housing without special materials may not perform well in highly corrosive or extreme temperatures.
Maintenance and Troubleshooting
Regular maintenance can significantly extend the life of pillow block bearings. Follow these tips for optimal performance:
- Lubrication: Regularly apply the correct type of lubricant as the manufacturer specifies. Over-lubrication or under-lubrication can cause premature bearing failure.
- Inspection: Periodically inspect bearings for signs of wear, noise, or vibration. Address any issues promptly to avoid extensive damage.
- Cleaning: Keep the bearing and surrounding area clean to prevent contamination from affecting performance.
- Replacement: Replace bearings with significant wear or damage to avoid machinery downtime.
Common Issues
- Noise: Can indicate misalignment, insufficient lubrication, or bearing damage.
- Vibration: Often caused by imbalance or misalignment of the shaft.
- Overheating: This may result from excessive load, insufficient lubrication, or friction.
Conclusion
Pillow block bearings are essential for mechanical systems, providing support and ensuring smooth rotating shaft operation. You can effectively utilise these bearings in various industrial applications by understanding their types, applications, and maintenance requirements. Stay updated with the latest trends to leverage new technologies and materials for improved performance.
FAQ on Sizing Pillow Block Bearings
How do I determine the correct shaft size for my pillow block bearing?
Measure the shaft diameter and ensure it fits the bearing bore. Consult the manufacturer’s specifications for recommended shaft tolerances.
What factors should I consider for bearing lubrication?
Consider the operating environment, load, speed, and maintenance schedule. Choose the appropriate type of lubricant (grease or oil) and apply it according to the manufacturer’s guidelines.
Can pillow block bearings handle axial loads?
The bearing type and design must be suitable for axial loads. Some bearings, like tapered roller bearings, are better suited for combined radial and axial loads.
How do I choose between solid and split housing?
A: Solid housings offer greater rigidity but are harder to maintain. Split housings allow easier bearing replacement and maintenance, making them ideal for applications with frequent bearing changes.