Additive manufacturing technology or 3D printing is a type of technology that uses successive layers of material to create 3D objects.
What is Additive Manufacturing (AM)?
The basic principle of Additive Manufacturing technology is that it uses CAD generated 3D model directly to fabricate a three-dimensional object by adding layer-upon-layer of material and fusing them.

More than enough statistics support the claim that the introduction of 3D Printing has revolutionised the industrial world in a way no other product has achieved this momentous success in the last 35 years.
Additive manufacturing vs Rapid prototyping vs 3D Printing
Although initially referred to as Rapid prototyping in a product development context, these technologies have made giant strides in recent years and moved from prototype to production-ready part manufacturing. Term 3D Printing is also widely used for these technologies, and MIT coined it for inkjet printing based on AM they invented in the 90s. Hence these terms do not effectively describe more recent technological advancements in the sector.
History of Additive Manufacturing
Chuck Hull, an American engineer of 3D Systems Corporation, is accredited with inventing 3D Printing in 1983, known as solid imaging process called stereolithography (3D Printing), the first commercial rapid prototyping technology and the STL file format. Thanks to Hull, his contribution of STL file format, digital layer slicing, and infill strategies are still being used today in many additive manufacturing processes.

Since then, many companies have invented and introduced new techniques. Because the technology is relatively new, companies that develop and introduce different techniques under new marketing terms, even though the core technique might be the same.
A technical committee under ASTM international finally defined these processes appropriately as Additive Manufacturing (AM), as the technology builds 3D parts by adding material compared to subtractive manufacturing.
As per ISO/ASTM standards, additive manufacturing technologies are divided into seven types according to the techniques used to create those layers, energy source and fuse material.
7 types of Additive manufacturing technologies
There are seven main additive manufacturing technologies viz Vat photopolymerisation, Material Extrusion, Material Jetting, Binder Jetting, Powder bed fusion, directed energy deposition, and Sheet lamination.
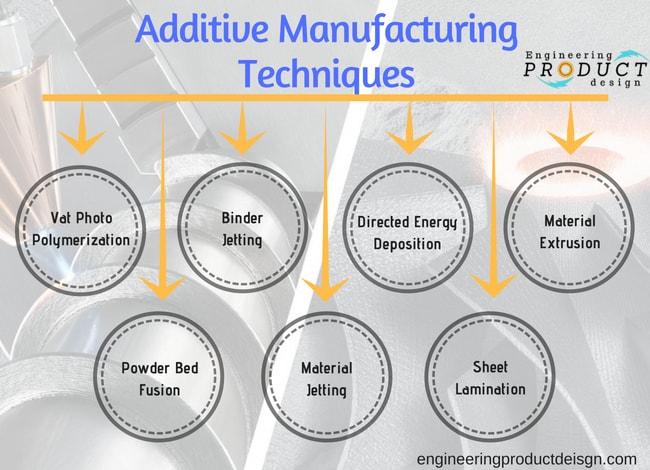
You can partially view the standards here.
Vat Photopolymerisation
This process uses a technique called Photopolymerization, in which radiation-curable resins or photopolymers are used to create three-dimensional objects by selectively exposing them to ultraviolet light. When exposed, these materials undergo a chemical reaction and become solid. Only plastics can be printed using these technologies.
There are three main types under this category – Stereolithography, Digital Light Processing and Continuous Digital Light Processing.
Binder jetting process
As the name implies, Binder Jetting selectively deposits the bonding agent, a binding liquid, to join the powder material to form a 3D part. This process is different to any other AM technology as it does not employ heat during the process like others to fuse the material.
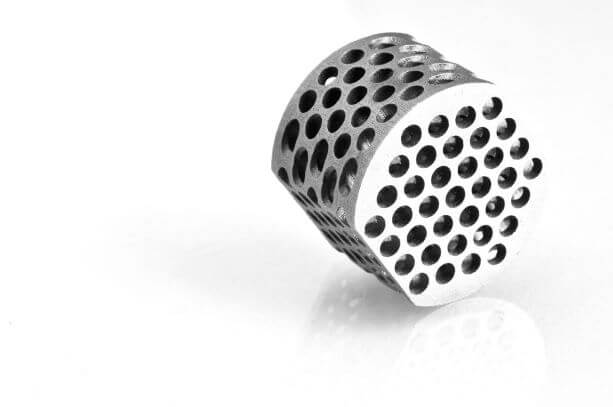

The print head and a powder spreader deposit alternating layers of bonding agent and build material to form a 3d object.
Directed energy deposition
Directed energy deposition technology uses focused thermal energy such as a laser, electron beam, or plasma arc to melt and fuse the material as they are deposited to create a 3d object. These are very similar to the welding process but very finely detailed.
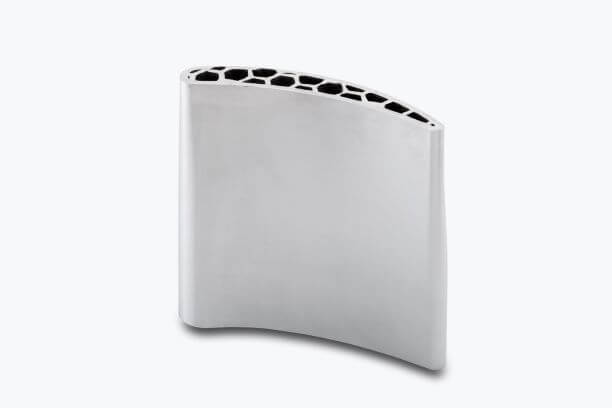

The geometric information included in a Computer-Aided Design (CAD) solid model is used by LENS 3D printers to autonomously direct the DED process as it builds up a part layer by layer.
The two main types of Directed energy deposition technologies are LENS and EBAM. EBAM uses an electron beam, and LENS uses a focused laser to melt the material.
Material extrusion
Material Extrusion is an additive manufacturing technique that uses a continuous filament of thermoplastic or composite material to construct 3D parts. Material extrusion was initially developed and patented by S. Scott Crump under Fused Deposition Modelling (FDM) in the 1980s.
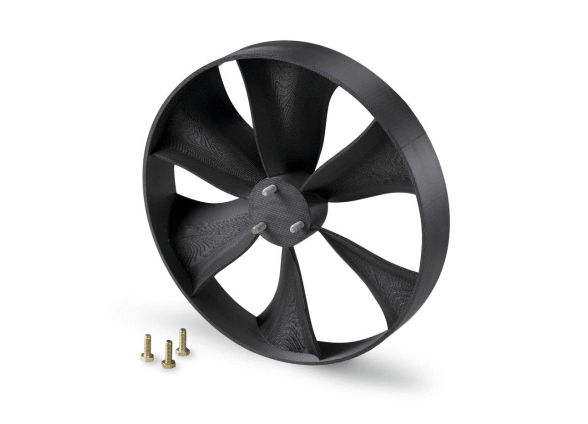

In this additive manufacturing technique, the continuous filament of thermoplastic is fed through a heated nozzle before being deposited layer by layer onto the build platform to create the object.
Material jetting
In material jetting, build material droplets are selectively deposited layer by layer into the build platform to form a 3D part.
This additive manufacturing technique is very similar to standard inkjet printers, where the material droplets are deposited layer by layer selectively to create a three-dimensional object. Once a layer is complete, its cured by ultraviolet light.
Powder material jetting includes the following commonly used printing technologies: UV cured Material Jetting, Drop On Demand (DOD), and NanoParticle Jetting (NPJ).
Powder bed fusion
Powder bed fusion is an Additive Manufacturing technique that uses either a laser or electron beam to melt and fuse the material to form a 3D geometry part. The Powder Bed Fusion includes the following commonly used printing technologies: Multi Jet Fusion (MJF), Direct metal laser sintering (DMLS), Electron beam melting (EBM), Selective heat sintering (SHS), Selective laser melting (SLM) and Selective laser sintering (SLS).

Powder bed fusion processes, especially selective laser sintering, are early industrial additive manufacturing techniques. This method uses a laser or electron beam to melt the powdered material and fuse them to create a solid object.
Sheet lamination
Sheet lamination technologies use sheets of material to create 3D objects by stacking them and laminating them using either adhesive or ultrasonic welding. Once the object is built, the unwanted areas of the sections are removed layer by layer.

Sheet lamination technology is an umbrella term for Ultrasonic Additive Manufacturing (UAM, Selective Deposition Lamination (SDL, and Laminated Object Manufacturing (LOM).
Advantages and disadvantages of additive manufacturing
Advantages of additive manufacturing
- AM can print complex 3D geometries with internal features without any tooling
- Reduced waste compared to machining
- Part can be printed directly from the 3D model without the need for a drawing
- Prototypes can be made quicker, allowing designers to check different iterations resulting in a quicker design cycle phase
- No or less tooling for smaller batches compared to traditional machining
- Production tooling can be printed
- Different materials can be mixed during the printing process to create a unique alloy
- Different sections of the part can be different variants of the same alloy
Disadvantages of additive manufacturing
- Because the technology is still in its infancy, the build process is slow and costly
- High production costs because of the equipment cost
- Various post-processing required depending on the type of additive manufacturing used
- Small build volume compared to other manufacturing part size such as sand casting
- Poor mechanical properties hence need post-processing
- Poor surface finish and texture compared manufacturing processes like CNC and investment casting.
- The strength of the parts is comparably weaker compared to manufacturing processes such as Die casting, Investment casting and CNC machining.
How Additive Manufacturing Technology works
Although the Additive manufacturing process flow varies between the 7 different additive manufacturing technologies it uses to create the 3D parts, each broadly follows these common steps to create the final part.
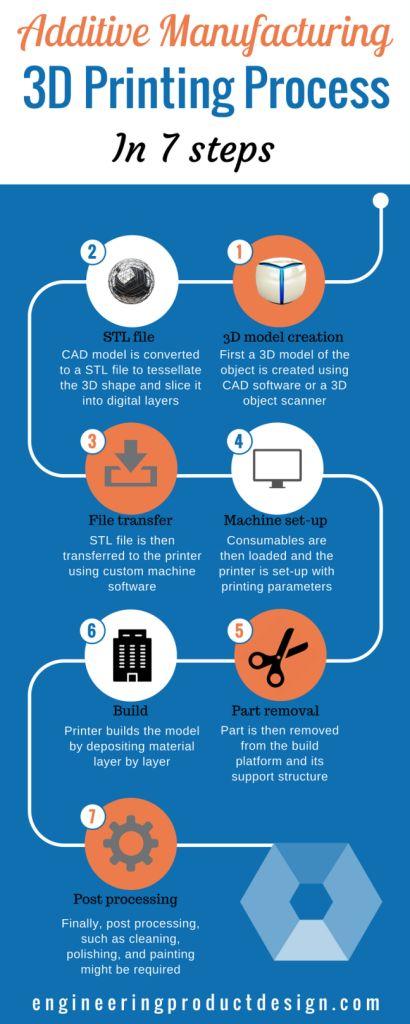
3D Model creation step
First, the designer creates a 3D model of the object to be printed using computer-aided design (CAD) software or a 3D object scanner. Since the part is a replica of the 3D model, every detail needs to be correct and fully defined its external geometry.
Although AM can print complex parts and gives the product designer more design flexibility than conventional manufacturing processes, there are still limitations and rules to adhere to when designing to achieve the best results.
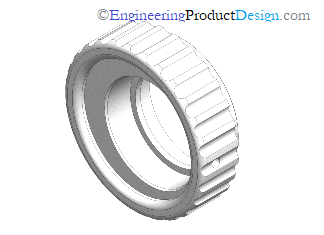
The design guides vary according to the additive manufacturing technology type and material selection. Equipment manufacturers and AM technology service providers have extensive design guides on designing parts. Refer to the types of AM technology and their manufacturers to find out more.
STL file creation step
Once the designer is happy with the design, the user converts the CAD file to a standard AM file format called standard tessellation language (STL), which 3D Systems developed in the late 80s for use in its Stereolithography (SLA) machines. You can read how the STL file is created and used for 3D Printing here.
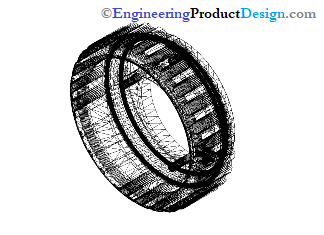
Most CAD software such as SolidWorks, Inventor and Catia can save any model as an STL file. However, all printer manufacturers have software to take any CAD formats and convert the files into an STL file.
As the name suggests, this will tessellate the 3D shape and slice the part into digital layers. The layer thickness dictates the final quality and depends on the machine and process.
STL file transfer step
STL file is then transferred to the printer, often using the custom machine software, where the model will be manipulated to orientate for Printing. Machine software might create its file with extra information at this stage, such as support structure and temperature.
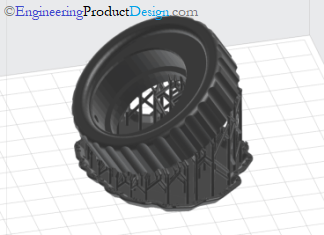
Machine set up
Each additive manufacturing technology and its variants have its own steps and requirements to set up a new printing job. Set up includes material selection, orientation, printer temperature, support structure and build platform levelling. It also involves loading print material, binders, and other consumables into the machine.
Machine software then converts the STL file information into G-code. G-code instructions are information for the actuators, such as motors, telling them where to move, how quickly to move, and what path to take.

Multiple parts can be set up to reduce the printing cost, and waste can also be minimised by choosing the correct orientation.
Part building
Once the build starts, it gradually builds the design one layer at a time. A typical layer is around 0.1mm in thickness, but depending on the technology and the material used, it can go down to 20 microns.

Depending on the build size, the printing machine, AM technology, material, and printing resolution, this build process could take hours or even days to complete.
Part removal
After building the part or multiple parts, in some cases, it may need a cooling-off period before removing the parts from the machine. Again depending on the machine and technology, removal could vary from simply peeling off the build platform in case of FDM to wire eroding from the build plate in DMLS.

Post-processing step
Almost all the additive manufacturing techniques will require some form of post-processing. Depending on the AM technology used and the part’s end-use, it varies from simple cleaning and polishing to machining and heating treating the part.
Finally, post-processing, such as cleaning, polishing, and painting, might be required
As discussed, each of the 7 Additive manufacturing technologies varies depending on the underlying technology it uses to lay material onto the build platform, material type, energy type use and post-processing.